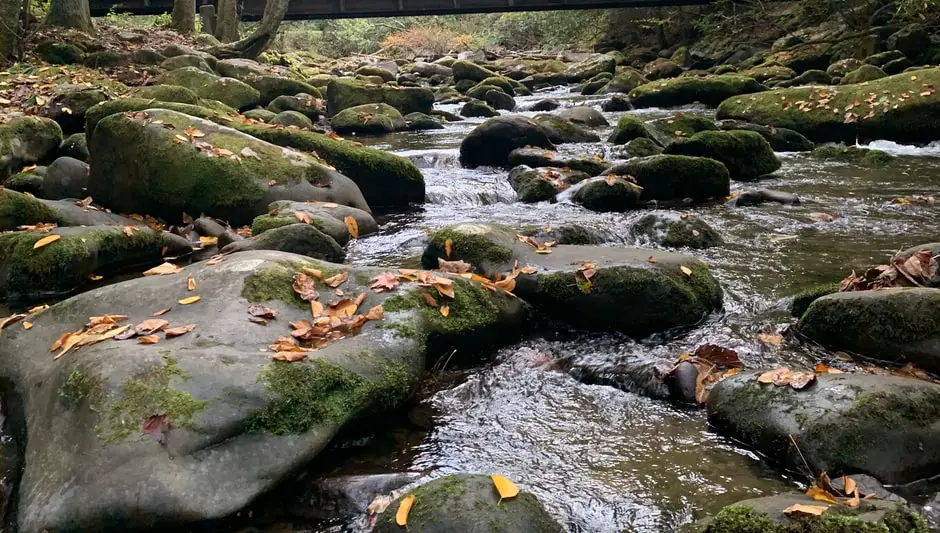
Sediment can smother insect larvae and fish eggs and destroy the spawning areas for fish. In the worst cases, it can kill fish. In addition to its effects on aquatic plants and animals, it can fill streams, lakes and ponds, block waterways and cause sewer backups. How much sediment is in a stream or pond depends on many factors, including the size of the stream and the amount of sediment in the water.
For example, a small stream may have little sediment, while a large stream could have a lot of it. A stream with lots of sediments may not be able to support fish or other aquatic life, so it may need to be drained. If the sediment level is too high, fish may be unable to find food and may die.
Table of Contents
What is sediment loss?
Water erosion leads to the loss of sand. Water erosion is the detachment and transport of soil particles by rainfall or irrigation water. This process is called sedimentation. Sedimentation is a major source of sediment in streams, rivers, and lakes, but it is not the only source.
In addition to precipitation, sediment is also transported by groundwater and surface water, as well as by wind and wave action. The amount of sediments in a stream depends on several factors, including the type of stream, the amount and location of water and sediment transport, how fast the water is moving and how long it has been moving.
For example, a small stream may have very little sediment, while a large stream with a lot of precipitation will have much more sediment than the same stream without precipitation. Because of this, it can be difficult to predict how much sediment will be lost from a particular stream.
How does land degradation affect soil quality?
They accelerate surface runoff and soil erosion, loss of organic matter and fertility and disruption in cycles of water, organic carbon and plant nutrients. The practices have a negative impact on the environment. When soil degrades, the processes that take place within it are disrupted, and this can lead to a range of negative impacts on the environment and human health.
The study, published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), is the first of its kind to examine the long-term effects of soil degradation on biodiversity and ecosystem services. It is based on a large-scale analysis of data collected by the US Geological Survey (USGS) and the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) over the past 40 years.
The researchers used the data to estimate the impacts of land-use change on plant and animal species richness and diversity, as well as soil carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus and water quality. They also looked at how these impacts were changing over time and how they could be mitigated.
How does sediment affect the water quality?
Sediments in suspension can have a significant impact on the water quality of a waterway because sediments decrease water clarity, which reduces visibility. Water clarity is the amount of water that can be seen from a distance of at least 1 meter. Sediments can also reduce the ability of fish and other aquatic organisms to filter out contaminants.
In addition to sediment, sediment-laden water can contain a variety of other contaminants, including bacteria, viruses, heavy metals, pesticides, herbicides, and industrial chemicals. These contaminants can affect the health of people and wildlife, as well as their ability to survive in the environment. For example, some of these contaminants are known to cause cancer in humans, while others can cause birth defects, reproductive problems, or other health problems in animals and humans.
How does sedimentation reduce water quality?
Sediment plays a major role in the transport and fate of pollutants and so is clearly a concern in water quality management. Toxic chemicals can become attached, or adsorbed, to sediment particles and then transported to and deposited in other areas. The pollutants may be absorbed by aquatic organisms when they are released into the environment. In addition, sediments can act as a barrier to the movement of nutrients and other contaminants.
Sediment can also be a source of organic material, which can be ingested by fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals. This can lead to a variety of health problems, including an increased risk of cancer and reproductive problems in humans. In addition to these health effects, sediment can affect the quality of drinking water, as well as the ability of plants and animals to adapt to changing environmental conditions.
How does sediment affect biodiversity?
Under unimpaired conditions, a dynamic equilibrium of erosion and sedimentation creates a diversity of aquatic sediment patches, which is vital for the maintenance of high habitat- and biodiversity. The deposition of fine-grained sediments in the water column affects the habitats of macroinvertebrate animals. In addition to the effects of sediment accumulation on the aquatic environment, sediment is also an important source of nutrients for aquatic plants and animals.
Sediment is a major component of marine food webs, and it plays a key role in nutrient cycling in marine ecosystems. For example, in coastal waters, the amount of dissolved organic carbon (DOC) and nitrogen (N) in sediment can be used to estimate the availability of these nutrients to marine organisms. In addition, it is important to understand the role that sediment plays in determining the distribution and abundance of fish and other marine species.
What is the result of sedimentation?
Sedimentation results in the formation of depositional landforms and the rocks that constitute the sedimentary record. In river valleys, the building up of land surfaces is called aggradation. The thickness of the land surface’s silt is what the rate of sedimentation is. Aggradation is a process in which sediment accumulates on the surface of a body of water, such as a river, lake, or ocean. Aggradation can occur in a variety of ways.
For example, sediment can be deposited by wind, rain, and snowmelt, as well as by the action of animals and plants. In some cases, the accumulation of sediments may be caused by a combination of these processes. Sediment can also be formed by natural processes, including erosion and deposition of sand and gravel.